Adenosine Trisphosphate, also known as the ‘currency of energy’ allows us to sprint, jump, walk, run, and think.
It’s ATP’s role to supply energy throughout the whole body, where it’s used for hundreds of different bodily functions.
In short, ATP captures energy from foods we eat, converting them into energy with the help of the mitochondria.
Therefore, the more ATP we have available, or the more efficiently ATP can be created will allow us to increase our performance.
Table of Contents
What Is ATP Adenosine Triphosphate?
As mentioned, ATP helps us to feel energized for mental activities, sports performance, while assisting in numerous bodily functions we don’t see, yet constantly take place.
This is all well and good, but what’s ATP made of?
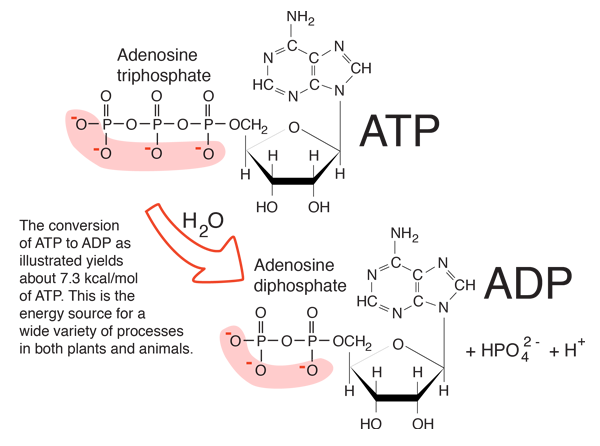
ATP, adenosine triphosphate, is made up of three phosphate molecules: adenine – ribose – trisphosphate. (01)
Trisphosphate is where energy is stored. This part of the equation contains three sections hence the name ‘trisphosphate‘.
Trisphosphate acts in a similar way to salts, where they store water (in this case energy) to then be distributed when needed – for the purpose of this explanation, this is in the form of energy.
The bonds between the second and the third phosphate within ‘trisphosphate’ contain energy.
When these are broken off using the enzyme ATPase, and water H2O, they provide energy throughout the body.
Question…what is ATPase? Here’s the answer:
“ATPases are a class of enzymes that catalyze the decomposition of ATP into ADP and a free phosphate ion. This dephosphorylation reaction releases energy, which the enzyme harnesses to drive other chemical reactions that would not otherwise occur. This process is widely used in all known forms of life.” (02)
Once the process of releasing the free phosphate molecule happens, the energy cycle is repeated, where the mitochondria use foods we eat to regenerate the second and third phosphate molecule. Thus allowing for more energy to be used.
How Can ATP Improve Performance?
Perhaps the most widely used ergogenic supplement to date, which has proven to be the most successful (Creatine) allows for more ATP to be created.
As previously mentioned, ‘trisphosphate’ is similar in its structure as salt, which can also be said for creatine.
Creatine’s role is to retain water in the cells of the muscle, allowing for more ATP to be created when needed – such as in sports. (03)
So… how can ATP create more energy, and how can we improve our ATP levels? Let’s dive int those questions right now.
How We Improve Our ATP Levels?
There are two common ways in which ATP can be increased. Firstly, by improving our fitness levels, and secondly, by using sports supplements such as creatine.
Let’s look at how ATP can be improved by increasing our fitness levels:
Increasing Fitness Levels
By exercising on a regular basis, the mitochondria becomes more efficient at producing ATP. Not only that, the mitochondria also increases in its ability to improve our sports performance by becoming more efficient in the way it assimilates foods into ATP. (04)
When we’re sedentary, the mitochondria is also inactive to a degree. However, when we begin to move, so will the mitochondria, where it begins to use the foods we’ve eaten (or stored in fat cells) to be converted into energy in the form of ATP.
Thus, as we take part in more activity, so will the amount of ATP that is created.
However, if our level of fitness are below optimal, taking part in longer duration exercises, or demanding power sports from the offset won’t necessarily mean our ability to create more ATP will be available.
First, we need to build up a solid foundation of fitness – which can take weeks or even months, where numerous adaptations need to take places. Such as improved hemoglobin, oxygen transportation, and the divide of fats, carbohydrates, ketones, and amino acids to be used as energy.
This is where the use of supplements may be of benefit – to speed up the process.
Supplementation
For power sports, creatine is proven to increase creatine phosphate stores in the muscles, which is a compound linked to powerful and explosive energy within the muscle. Such as sprints, and heavy single repetitions for example.
In short, any explosive movement requires creatine, which assists the mitochondria and ATP in providing these bursts of energy.
Therefore, supplementing with creatine for several days has been shown to improve performance output. (05)
Creatine has also been documented as safe to use in the long term. Meaning, it can be taken throughout the year when training or taking part in sports. This makes creatine a viable option for improving ATP levels while increasing training capacity and fitness levels.
Read More: In-depth Look At Creatine
Other Benefits To ATP Production
While more ATP is generally the desired outcome when sports performance is concerned, there are other reactions and by-products created from ATP that can also benefit us in other ways.
These may include the improvement of sleep and restoration, which is exactly what happens once ATP is created, leaving behind a waste product that helps the body to rejuvenate itself – Adenosine.
What Is Adenosine?
Adenosine is the byproduct of ATP waste, hence the name adenosine – coming from adenosine triphosphate. (06)
It helps the blood vessels to dilate, allowing for more oxygen and nutrients to be shuttled around the body when there may be restrictions – such as those put on the body during intense exercise.
Adenosine has shown to help induce a more restful sleep – non-REM sleep to be exact. This is the period of sleep that accounts for roughly 85% of our total night’s sleep.
Why is non-REM sleep so important?
This is the stage where our mind and body repairs itself the most. While REM is important, non-REM is considered the most beneficial for reset and restoration.
What Does Adenosine Do?
Adenosine is a hypnogenic substance “producing or concerned with the production of sleep”. It’s a compound found naturally in the body which is linked to the essential component in energy production ATP adenosine trisphosphate. (07)
Adenosine receptors are found in large amounts throughout the central nervous system (CNS). Adenosine then works to depress neuronal activity, which is important for healthy levels of sleep and recovery.
With ‘prolonged wakefulness’, a sharp rise is then seen in adenosine, which then triggers sleep. This happens due to adenosine being a wastage bi-product of adenosine-trisphosphate. (08)
Increases Quality Of Sleep and Restoration
Adenosine trisphosphate works to supply the body and mind with energy, where it rejuvenates, creating more ATP.
With the increase in production in ATP, then, adenosine begins to build up in the mind, which is what makes us fall asleep – along with other important chemicals such as dopamine etc.
Adenosine doesn’t just build up in the mind after prolonged wakefulness, it also spikes during and after stress, either mental or physical. This is why you may feel sleepy or tired after an exam, hard days work, or a workout to name a few.
Where Does Adenosine Come From?
As already discussed, adenosine is created as a by-product of adenosine-trisphosphate.
“Adenosine is produced by the degradation of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the molecule that serves as the “energy currency” for the body’s various cellular functions.” (09)
In short, adenosine is created when ATP is rejuvenated and re-cycled – it builds up in the mind and body once as ATP is being created.
What Contributes To Low Levels Of ATP?
Issues with being overweight, living a sedentary lifestyle, a diet which puts a lot of stress on the body and a lack of sleep are all contributors to low energy levels.
Obesity:
Being overweight puts a strain on the body, especially when we’re required to perform any type of exercise. Carrying excess weight means the heart, lungs, and other internal organs, not to mention our muscles, will require additional energy to supply blood and oxygen throughout the body for activity to happen.
As weight increases in the form of body fat, so will the energy requirements to walk, run, swim, cycle and move in general. Therefore, by losing weight, the body then becomes more efficient at supplying ATP throughout the body. (10)
This is due to their being less body fat, which equates to less blood and oxygen needed to be transported around the body. Which may be seen as an unnecessary energy requirement, especially where physical performance is concerned.
Oxidative Stress:
Stress comes in many forms, from physical induced stress from exercise, emotional stress from work, and day-to-day commitments. Not to mention the stress that’s put on our bodies from the foods we eat. (11)
By lowering stress levels, either by making smaller adaptations to exercise over a longer period, meditating to reduce external stressors out of our control, or by eating a diet that contains more whole foods, then we may see a greater increase in energy.
Sleep:
Sleep is crucial for energy, without it we would begin to deteriorate, our moods will change for the worse, our attention span will decrease, and our physical performance will begin to take a nosedive if not mitigated quickly. (12)
A lack of sleep puts a large strain on the body and mind. As discussed in this article, when ATP is created, so is adenosine, which is responsible for inducing sleep, most importantly non-REM sleep which is known to heal and rejuvenate the body.
Therefore, getting adequate sleep, especially if you’re taking part in physical training, or you’re under more emotional stress than normal, is an important step in making sure your body can produce energy via ATP in the correct ways.
Conclusion
ATP the ‘currency of energy’ found in all living creatures, even plants, is vital for our health, brain, and sports performance.
Without adequate levels of ATP, we simply wouldn’t be able to function efficiently. Therefore, improving our fitness levels, or using sports supplements may be an option to help increase our energy – to reach a specific goal.
As discussed, low levels of ATP may be due to stress, or a diet lacking in the right amino acids, vitamins, and minerals. Also, if you’re overweight, this may cause a strain on your body, thus preventing for optimal energy levels to be created.
In summary: ATP allows for more energy to be produced, helping you become more explosive and energized.
Improve your fitness levels, and you’ll find that your energy levels will feel much higher on a daily basis.
To do this, taking part in exercise while eating a diet rich in nutritious colorful foods, while mitigating stress is one way.
The other way is to use sports supplements such as creatine, a safe and proven sports ergogenic widely used around the world by sporting professionals.
Resources:
(01) Wikipedia – Adenosine triphosphate. (source)
(02) Wikipedia – ATPase. (source)
(03) Creatine Supplementation and Sporting Performance. (source)
(04) ScienceLearning.org – Energy for exercise. (source)
(05) International Society of Sports Nutrition position stand: creatine supplementation and exercise. (source)
(06) Sleep-Wake Sensitive Mechanisms of Adenosine Release in the Basal Forebrain of Rodents: An In Vitro Study. (source)
(07) Role of adenosine in behavioral state modulation. (source)
(08) Wikipedia – Adenosine. (source)
(09) The Molecules That Build up And Make You Sleep. (source)
(10) Molecular implications of adenosine in obesity. (source)
(11) Oxidative stress and its relationship with adenosine deaminase activity in various stages of breast cancer. (source)
(12) The Role of ATP in Sleep Regulation. (source)

Leave a Reply